Hepatitis In Children: What You Need To Know
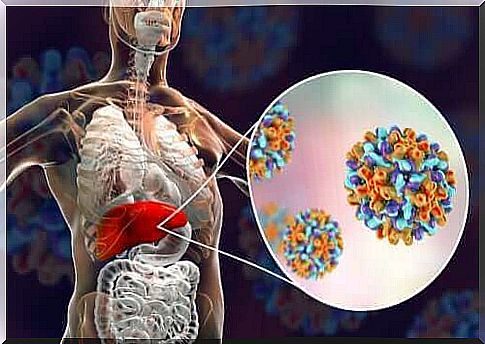
Hepatitis in children, as in adults, is caused by inflammation of the liver. The liver is a gland on the right side of the abdomen and acts as a system of cleansing the body of toxins.
It also produces several vital substances, such as those responsible for blood clotting, and is involved in the digestive process. The problem begins when inflammation occurs, because then the liver cannot function properly.
Although the incidence of hepatitis in children has decreased with vaccines against some types of viruses that cause it, it remains a serious health problem for the population.
Especially because this infection may go unnoticed and yet it leads to complications at some point in life. Usually hepatitis is caused by viruses that are related to the liver.
In this article, we’ll explain more about hepatitis in children and the most common causes of hepatitis.
What causes hepatitis in children?
As we mentioned, hepatitis in children is caused almost entirely by viruses. They can be grouped into a family known as hepatitis viruses.
The most important of these are the hepatitis A, B and C viruses, although there are others, such as D and E, which are less common, however.
The most common cause of hepatitis in children is the hepatitis A virus (HAV). The disease it causes is usually mild and self-limiting. For example, it can be stated that in Spain it affects almost 5% of children.
This virus spreads via the fecal-oral route (what happens, for example, when we do not wash our hands well after using the toilet).
Most of the cases occur in places where proper hygienic conditions have not been ensured. The water we drink that is not properly treated and purified can contain traces of faeces that carry the virus.
Hepatitis in children with HAV usually goes unnoticed because the clinical symptoms are not serious. However, this means that an epidemic or increased infection may occur among other family members.
Hepatitis B virus
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is much more serious. It’s not that the infection causes more pronounced symptoms initially, but the fact that it tends to become chronic. This virus is spread mainly because the mother transmits it to the baby during pregnancy or childbirth.
In addition, in many cases, the type B virus spreads during adolescence. This may include adolescents who are addicted to injecting drugs such as heroin. Infection can occur even during tattooing or piercing without proper hygiene measures.
Hepatitis C virus
Nowadays, the cause of hepatitis in children is much less frequently caused by the type C virus (HCV). Why? Because hygiene and safety measures have improved. It is worth knowing that this virus is also transmitted parenterally.
The vast majority of cases are situations when the child becomes infected from the mother. However, it is much less likely that the mother will infect the infant.
However, HCV also tends to become chronic. Nearly 75% of infections eventually lead to cirrhosis or liver cancer. Therefore, it is important to prevent this and initiate treatment promptly.
Hepatitis in children: what are the symptoms?
As we mentioned, hepatitis in children may go unnoticed. Its symptoms are quite nonspecific and, in some cases, mild. For example, inflammation can show up as a feeling of tiredness and a general feeling of being unwell.
In some cases, sick children suffer from jaundice. Then the skin and eyes turn yellowish. There may also be other symptoms, such as:
- fever – not very high in hepatitis A and slightly higher in the initial stage of hepatitis B,
- vomiting ,
- stomach pain, especially around the liver
- loss of appetite and weight loss.
To protect children from some types of hepatitis, it is important to follow the immunization schedule.
Also, if there are any warning signs, be sure to visit your doctor and ask him to do all the necessary tests to monitor your baby’s health or treat it appropriately if there is an infection.